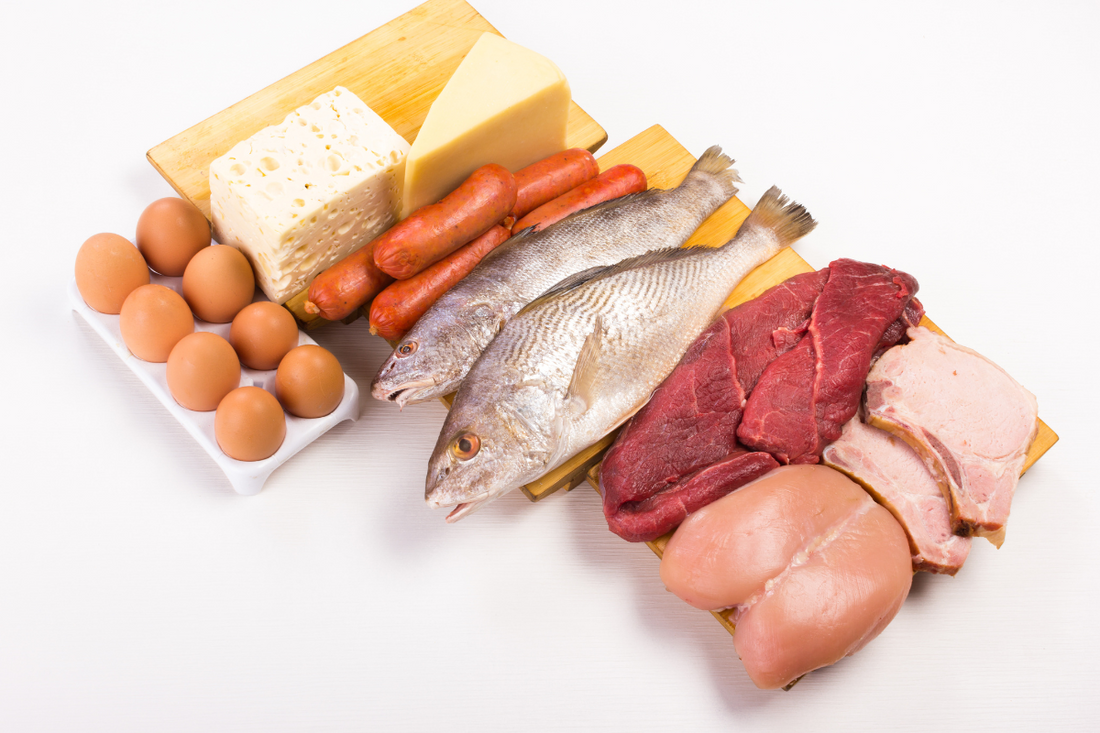
Have you ever wondered why protein is often referred to as the cornerstone of a healthy diet?
From fueling your workouts to supporting your immune system, the function of protein in the body is vast and indispensable since it forms muscles, tissues, enzymes, and hormones.
This blog discusses protein's function, daily needs, advantages, and how to eat protein-rich foods for the best health. Understand protein's responsibilities and advantages to make smart dietary choices and suit your body's demands.
What are the major functions of protein?
Along with carbohydrates and fats, protein is one of the three macronutrients needed for growth, repair, and maintenance. Long sequences of amino acids are used to construct and repair tissues, manufacture enzymes and hormones, and maintain immunological function. The body needs protein for several physiological processes:
1. Muscle Growth and Repair:
Protein provides essential amino acids necessary for muscle repair and growth. This is vital for athletes and individuals engaged in resistance training as it helps rebuild muscle tissues after physical activity, enhancing strength and endurance.
2. Supports Weight Management:
Protein helps regulate appetite by increasing the levels of hormones that promote fullness, such as GLP-1, peptide YY, and cholecystokinin, while reducing levels of the hunger hormone ghrelin. This aids in weight management and can contribute to a healthier body composition.
3. Hormone and Enzyme Production:
Proteins are integral in synthesising hormones like insulin and thyroid hormones, which regulate blood sugar levels and metabolism. Additionally, enzymes, which are proteins, facilitate essential biochemical reactions in the body, such as digestion and energy production.
4. Structural and Immune Support:
Proteins like collagen peptides provide structural support to cells and tissues, contributing to the health of skin, hair, nails, and bones. They are also essential for the immune system, as they help produce antibodies that combat infections and maintain overall health.
5. Metabolism and Cellular Function:
Protein plays a crucial role in metabolism, as it has a higher thermic effect compared to fats and carbohydrates, promoting increased energy consumption. It also helps repair damaged cells, supports muscle contraction, and regulates overall metabolic processes, contributing to the body's efficient functioning.
Daily Required Protein Intake for Men and Women
The amount of protein required varies based on factors such as age, gender, and activity level. The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) provides a general guideline:
- Men: 56 grams per day
- Women: 46 grams per day
How to add protein in your regular diet?
To maximise the benefits of protein, it's essential to include a variety of protein-rich foods in your diet. Here are some tips:
- Plan Your Meals Around Protein: Start each meal with a high-protein food source. For breakfast, include protein-packed eggs like bright orange yolk eggs, or Greek yoghourt. For lunch and dinner, opt for lean meats, fish, or high protein veg food like lentils and chickpeas.
- Include Protein Snacks: Keep high-protein snacks like nuts, seeds, and cheese handy. If you're on the go, high-protein snacks like protein bars or shakes made with the best protein powder can be convenient.
- Use Protein Supplements Wisely: If you're struggling to meet your protein needs through food alone, consider using a high-quality best protein powder like whey or casein. Collagen peptides can also be beneficial for joint and skin health.
- Incorporate Variety: Include both animal and plant-based proteins in your diet. Egg whites, whole eggs, dairy, tofu, tempeh, and quinoa are excellent choices.
- Monitor Your Intake: Using a nutrition app can help track your protein intake and ensure you're not over or under-consuming this crucial nutrient.\
High protein food list
|
Food |
Protein (g/100g) |
Protein (g/serving) |
% DRV* |
|
Whole Egg |
14.1 |
7 g (1 egg or 50 g serving) |
12% |
|
Salmon |
25.3 |
25.3 g (100 g serving) |
44% |
|
Gouda Cheese |
25.3 |
12.7 g (50 g serving) |
22% |
|
Chicken Breast |
28.4 |
21.3 g (75 g serving) |
37% |
|
Quinoa (Cooked) |
4.4 |
6.6 g (150 g serving) |
11% |
|
Rolled Oats |
10.9 |
5.5 g (50 g serving) |
9% |
|
Milk (Semi Skimmed) |
3.4 |
6.8 g (200 ml serving) |
12% |
|
Nut Mix |
23.8 |
5.9 g (25 g serving) |
10% |
|
Milk (Full Fat) |
3.5 |
7 g (200 ml serving) |
12% |
|
Red Kidney Beans |
8.6 |
8.6 g (100 g serving) |
15% |
|
Goat's Cheese |
21.1 |
10.6 g (50 g serving) |
18% |
|
Pasta (Cooked) |
5.5 |
8.3 g (150 g serving) |
14% |
Conclusion
Protein is essential for muscular building and immunological support. Understanding the function of protein and the benefits of protein can help you make informed dietary choices that promote health and well-being. With high levels of essential nutrients like Omega-3, Vitamin D, and amino acids, Eggoz eggs provide the ideal blend of quality protein and health benefits. Remember to balance your diet with sufficient high fibre food and other nutrients to support overall health. By doing so, you can enjoy the benefits of a high-protein diet, whether your goal is to build muscle, lose weight, or simply feel your best.